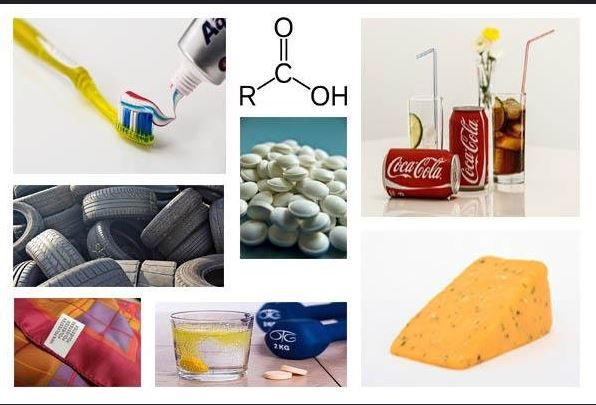
Carboxylic acids are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (–COOH). This functional group comprises a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to a hydroxyl group (–OH). The structure of carboxylic acids gives them unique chemical properties, including their acidic nature. The acidity is attributed to the ability of the carboxyl group to donate a proton (H+), forming a carboxylate anion (RCOO⁻) in solution.

The Role of Carboxylic Acids
Importance in Organic Chemistry
Carboxyl Compounds play a crucial role in organic chemistry due to their versatile chemical behavior. They are involved in a wide range of reactions, including esterification, where they react with alcohols to form esters, and amidation, where they react with amines to produce amides. These reactions are fundamental in the synthesis of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and polymers.
Biological Significance
In biological systems, carboxylic acids are vital components of many metabolic pathways. For example, fatty acids, which are long-chain Carboxyl Compounds , are key in energy storage and cellular function. Citric acid, another carboxylic acid, plays a central role in the Krebs cycle, a crucial metabolic pathway for energy production in cells.
Applications in Industry
Carboxylic compounds are used extensively in industry. Acetic acid, for instance, is a fundamental ingredient in vinegar and is used in the production of various chemicals and polymers. Benzoic acid is used as a preservative in food and pharmaceuticals, while other carboxylic acids serve as intermediates in the synthesis of dyes, surfactants, and lubricants.
Environmental Impact and Regulation
Carboxyl Compounds also have environmental and regulatory considerations. Some Carboxyl Compounds can be hazardous if not handled properly. For example, acetic acid at high concentrations can be corrosive, and its release into the environment needs to be controlled. Regulations are in place to manage the safe handling, storage, and disposal of carboxylic acids to minimize their environmental impact.