Medicinal chemistry plays a crucial role in developing new pharmaceuticals that target specific diseases and conditions. This article explores the principles of medicinal chemistry, emphasizing drug design and function to improve human health.
Medicinal Chemistry- Drug Design and Function
Fundamentals of Medicinal Chemistry
Medicinal chemistry focuses on understanding the interactions between chemicals and biological systems:
- Objectives: Developing safe and effective drugs through molecular design and optimization.
- Biological Targets: Targeting proteins, enzymes, receptors, and pathways involved in disease processes.
Drug Discovery Process
The process of discovering new drugs involves several stages:
- Target Identification: Identifying specific molecular targets associated with disease.
- Lead Identification: Finding initial chemical compounds that interact with the target.
- Lead Optimization: Modifying lead compounds to enhance potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties.
Principles of Drug Design
Effective drug design integrates knowledge from chemistry, biology, and pharmacology:
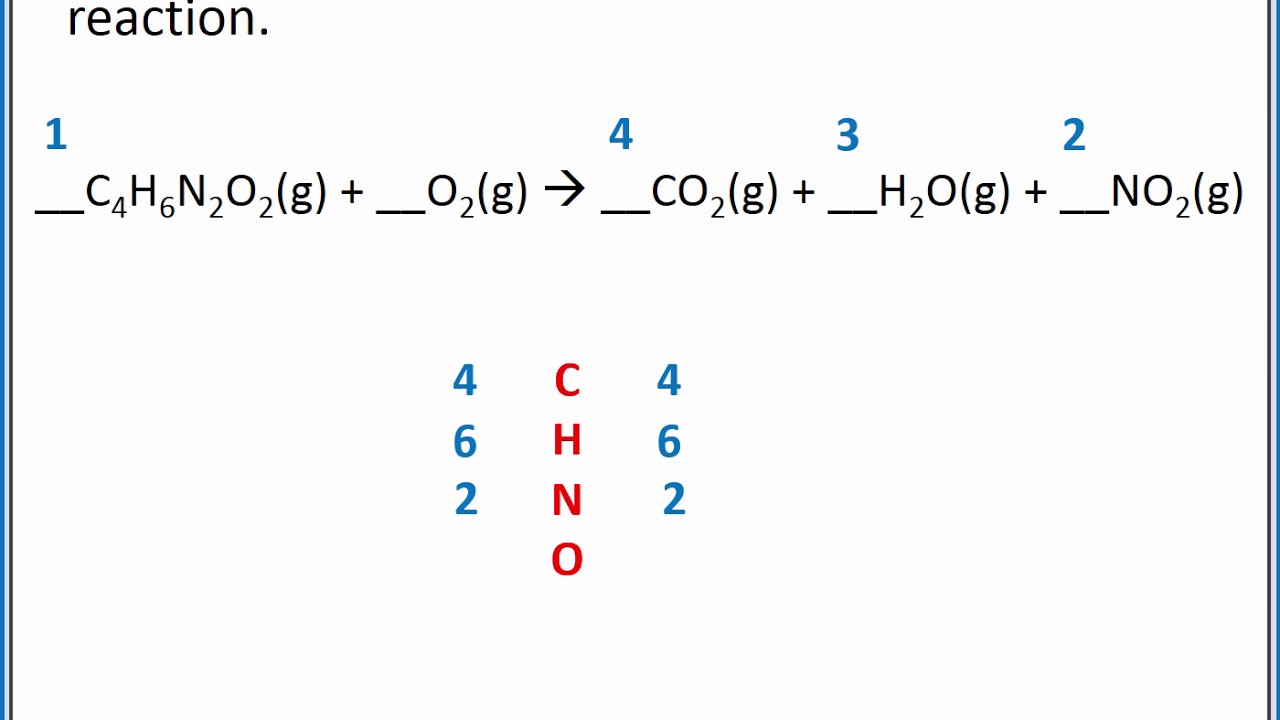
- Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR): Studying how changes in chemical structure affect biological activity.
- Bioisosterism: Substituting atoms or groups in a molecule to optimize pharmacological properties.
- Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD): Using computational methods to model molecular interactions and predict drug behavior.
Drug Development and Testing
Once potential drug candidates are identified, they undergo rigorous testing:
- Preclinical Studies: Assessing safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics in animal models.
- Clinical Trials: Testing drugs in human subjects to evaluate safety and effectiveness.
- Regulatory Approval: Obtaining approval from regulatory agencies based on clinical trial results.
Role of Medicinal Chemists
Medicinal chemists contribute expertise in various aspects of drug discovery and development:
- Synthetic Chemistry: Designing and synthesizing novel compounds with desired biological activity.
- Analytical Chemistry: Developing methods to analyze drug compounds and metabolites.
- Medicinal Chemistry Teams: Collaborating with biologists, pharmacologists, and clinicians to advance drug projects.
Challenges and Innovations
The field of medicinal chemistry faces challenges and opportunities:
- Drug Resistance: Addressing resistance mechanisms in pathogens and cancer cells.
- Emerging Technologies: Utilizing genomics, proteomics, and artificial intelligence to accelerate drug discovery.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Future Directions in Medicinal Chemistry
Future trends focus on precision medicine and novel therapeutic approaches:
- Biologics and Therapeutic Antibodies: Developing biologically-derived drugs for targeted therapies.
- Gene Editing and RNA Therapeutics: Harnessing gene editing tools and RNA-based treatments for genetic disorders and cancers.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical Chemistry combines scientific disciplines to design, discover, and develop drugs that treat diseases effectively and safely. By advancing our understanding of molecular interactions and employing innovative technologies, medicinal chemists continue to shape the future of healthcare.