Metals are a fundamental part of our daily lives, found in everything from the buildings we live into the cars we drive. The chemistry of metals involves studying their properties and how they react with other substances. This article will explore the unique properties of metals, such as conductivity, malleability, and reactivity. We’ll also look at common chemical reactions involving metals and their practical applications.
Chemistry of Metals: Properties and Reactions
Key Properties of Metals
Conductivity
One of the most notable properties of metals is their ability to conduct electricity and heat. This characteristic is due to the presence of free electrons that move easily within the metal’s structure. For instance, copper is widely used in electrical wiring because it is an excellent conductor of electricity. Similarly, metals like aluminum and silver are also known for their high conductivity.
Malleability and Ductility
Metals are malleable, meaning they can be hammered or rolled into thin sheets without breaking. They are also ductile, which means they can be drawn into wires. These properties are crucial in manufacturing and construction, allowing metals to be shaped into various forms for different uses. For example, the malleability of aluminum makes it ideal for producing cans and foil.
Luster and Appearance
Most metals have a shiny appearance, known as luster, which makes them attractive for decorative purposes. This luster is due to metals’ ability to reflect light. Gold and silver are often used in jewelry because of their appealing luster and resistance to tarnishing.
Reactivity of Metals
Oxidation and Corrosion
Many metals react with oxygen in the air to form oxides, a process known as oxidation. For example, when iron reacts with oxygen, it forms iron oxide, commonly known as rust. This reaction is not only a chemical change but also a concern for the longevity of metal structures. Metals like aluminum form a protective oxide layer that prevents further corrosion, while others, like iron, may require coatings or treatments to prevent rust.
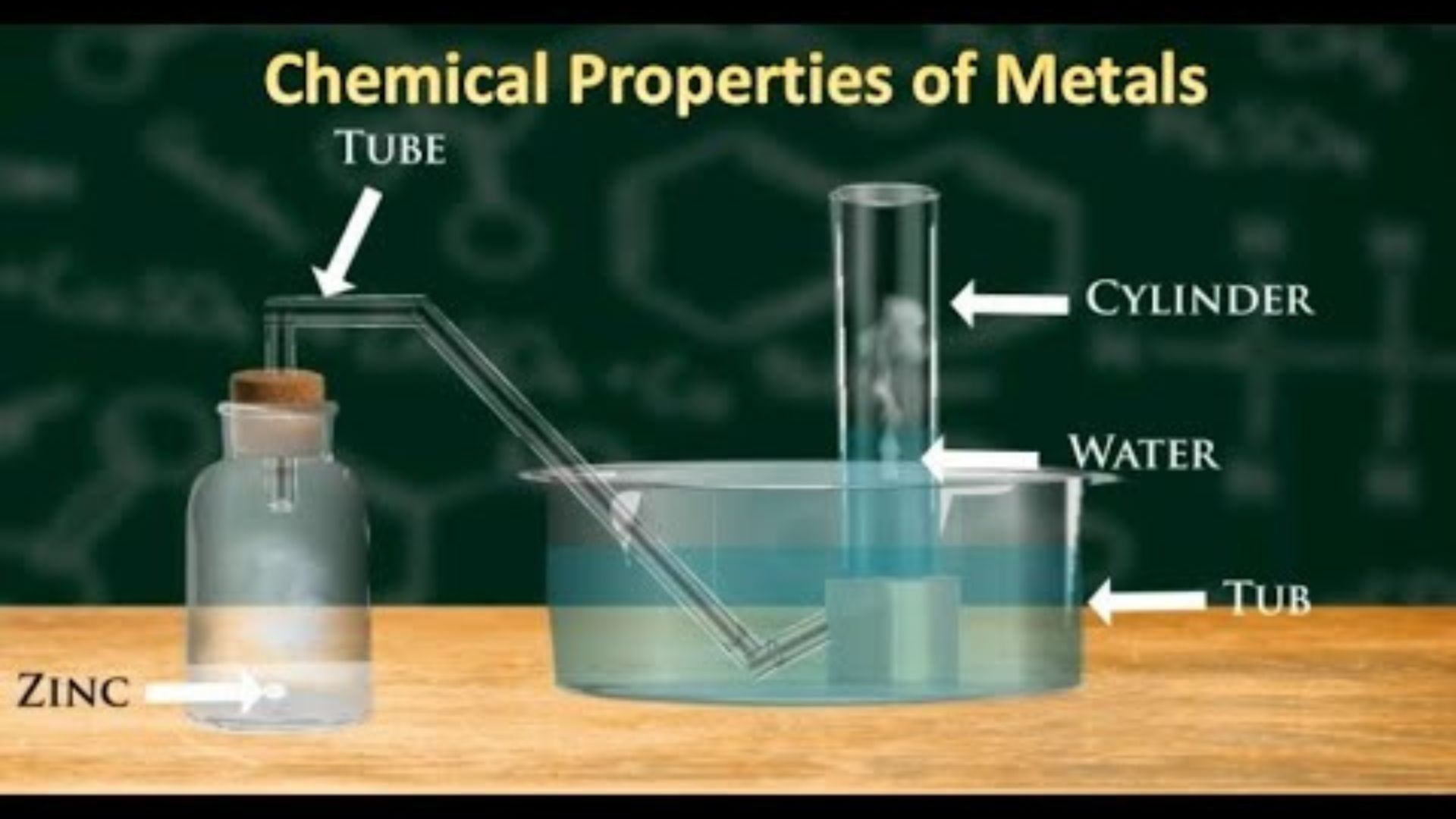
Acid Reactions
Metals also react with acids in a characteristic way, often producing hydrogen gas. For instance, when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are produced. This type of reaction is useful in various industrial processes, such as metal plating and refining.
Alloy Formation
Metals can be mixed with other elements to form alloys, which have enhanced properties compared to pure metals. For example, steel, an alloy of iron and carbon, is stronger and more durable than pure iron. Alloys are used extensively in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries due to their improved strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Practical Applications of Metal Chemistry
Electronics and Technology
The excellent conductivity of metals makes them indispensable in the electronics industry. Metals like copper, gold, and silver are used in electronic circuits, connectors, and other components. The development of new alloys and metal-based materials continues to drive advancements in technology, including in fields like renewable energy and electric vehicles.
Construction and Infrastructure
Metals are a cornerstone of modern construction. Steel, in particular, is widely used in building structures, bridges, and infrastructure projects due to its strength and versatility. The ability to alloy metals allows for the creation of materials with specific properties tailored to particular applications, such as weather resistance or flexibility.
Medical and Biomedical Uses
Metals also play a crucial role in medicine and healthcare. Titanium, for example, is used in medical implants due to its biocompatibility and strength. Silver, known for its antibacterial properties, is used in wound dressings and medical devices to prevent infections.
Conclusion
The chemistry of metals is a fascinating field that combines fundamental science with practical applications. Metals’ unique properties, such as conductivity, malleability, and reactivity, make them invaluable in various industries. Understanding these properties and reactions allows us to harness metals’ potential in innovative and beneficial ways. From everyday products to advanced technologies, metals continue to be a vital part of our world.




