Chemical safety is a critical aspect of laboratory work, ensuring that hazardous substances are managed properly to prevent accidents and protect the health of researchers and the environment. Adhering to safety protocols is essential for maintaining a safe working environment and complying with regulations. This guide provides an overview of key chemical safety and handling protocols, including best practices for storage, usage, and disposal of chemicals.
1. Understanding Chemical Safety
1. Importance: Chemical safety protocols are designed to minimize the risks associated with handling hazardous substances. Proper safety measures help prevent accidents, injuries, and environmental contamination.
2. Regulatory Standards:
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Establishes standards for workplace safety, including chemical handling.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): Regulates the disposal and environmental impact of hazardous chemicals.
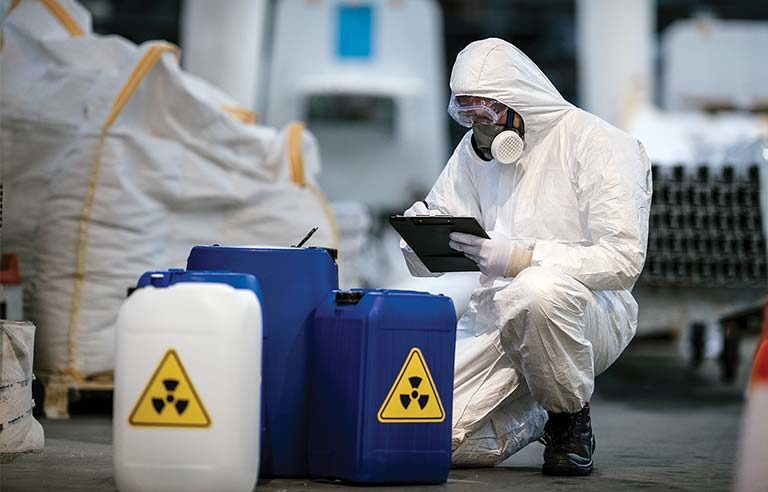
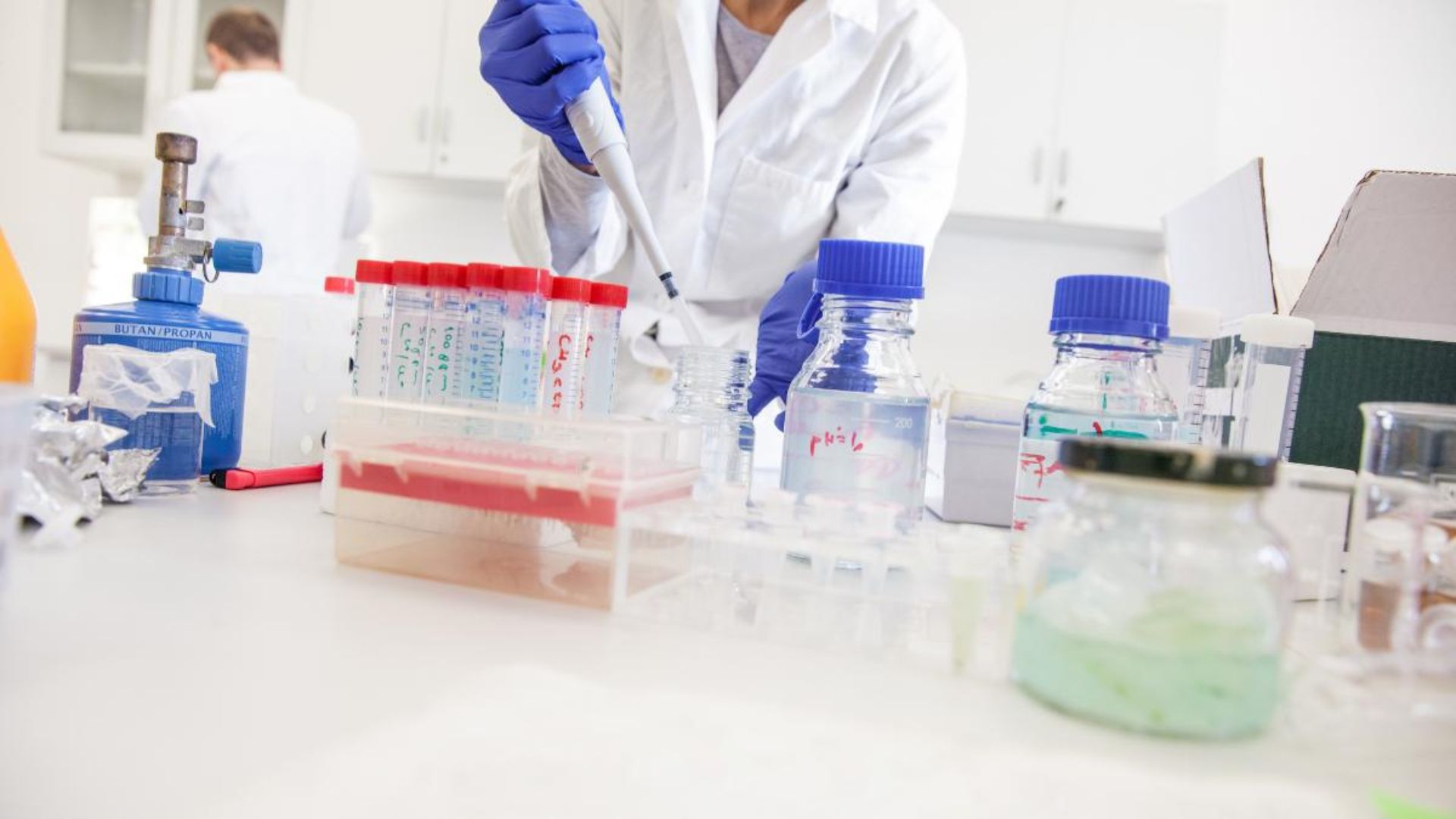
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
1. Types of PPE:
- Gloves: Protect hands from chemical exposure. Choose gloves made from materials resistant to the specific chemicals being handled.
- Safety Goggles: Shield eyes from splashes and airborne particles. Ensure goggles fit securely and are compliant with safety standards.
- Lab Coats: Provide protection against spills and splashes. Use lab coats made from materials that are resistant to chemical penetration.
- Face Shields: Offer additional protection for the face and neck in situations involving high-risk chemicals or reactions.
- Respirators: Necessary for handling volatile chemicals or working in environments with poor ventilation. Select appropriate respirators based on chemical exposure risks.
2. Proper Use:
- Inspect PPE: Regularly check for wear and tear. Replace damaged or worn-out equipment immediately.
- Follow Guidelines: Use PPE as recommended by safety data sheets (SDS) and laboratory protocols.
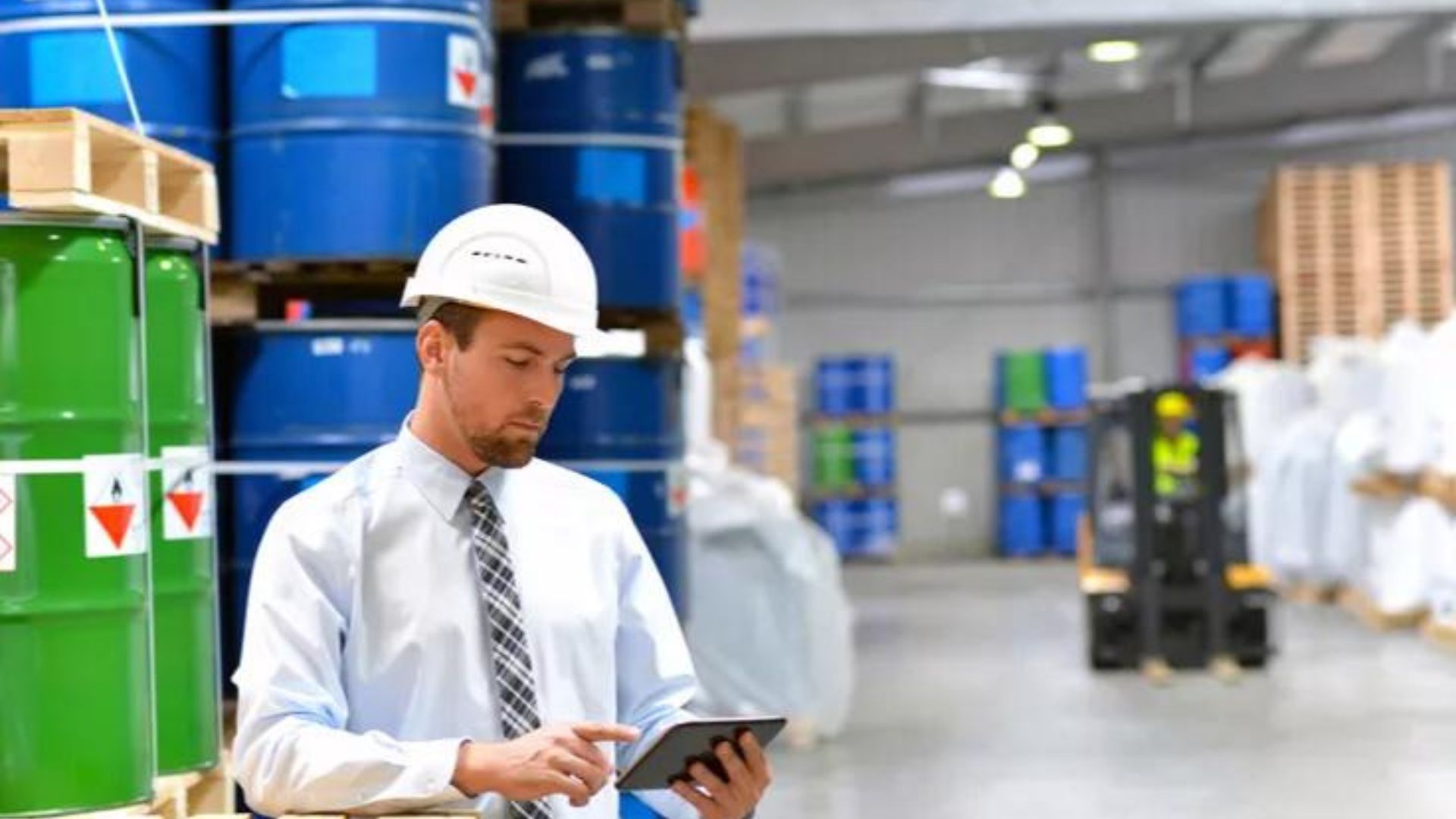
3. Chemical Storage

Chemical Safety
1. General Guidelines:
- Labeling: Clearly label all chemical containers with the chemical name, hazard symbols, and handling instructions.
- Segregation: Store chemicals according to their hazard classifications. Keep incompatible chemicals separate to prevent dangerous reactions.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in storage areas to minimize the buildup of harmful fumes. Use fume hoods or local exhaust systems if necessary.
- Temperature Control: Store chemicals at recommended temperatures to prevent degradation or dangerous reactions.
2. Specific Storage Requirements:
- Flammable Chemicals: Store in flame arrestors or safety cabinets designed for flammable materials. Keep away from ignition sources.
- Corrosive Chemicals: Store in corrosion-resistant containers and use secondary containment to protect surfaces and equipment.
- Toxic Chemicals: Store in secure, well-ventilated areas with restricted access to minimize exposure risks.
4. Chemical Handling and Usage
1. Handling Procedures:
- Read SDS: Review the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for each chemical to understand its hazards, handling requirements, and emergency procedures.
- Use Proper Techniques: Follow recommended techniques for transferring, mixing, or using chemicals to minimize spills and exposure.
- Avoid Eating/Drinking: Never eat, drink, or apply cosmetics in the laboratory to avoid contamination.
2. Safe Practices:
- Work in Well-Ventilated Areas: Use fume hoods or other ventilation systems when working with volatile or hazardous chemicals.
- Use Appropriate Containers: Transfer chemicals using clean, compatible containers to prevent reactions or contamination.
- Label Containers: Ensure all containers used for chemicals are clearly labeled with their contents and associated hazards.
5. Chemical Disposal
1. Disposal Methods:
- Follow Regulations: Dispose of chemicals according to local, state, and federal regulations. Consult with waste disposal experts if necessary.
- Segregated Disposal: Separate chemicals into appropriate waste categories (e.g., flammable, corrosive, toxic) for safe disposal.
- Use Designated Containers: Place waste chemicals in properly labeled, approved containers for disposal. Ensure containers are securely closed.
2. Emergency Procedures:
- Spills: Have spill kits readily available and follow procedures for cleaning up chemical spills. Evacuate the area if necessary and report the spill to appropriate authorities.
- Exposure: In case of chemical exposure, follow first aid protocols outlined in the SDS. Seek medical attention immediately if needed.
- Fire: Be familiar with the location and use of fire extinguishers and fire alarms. Follow the laboratory’s fire safety plan in case of an emergency.
6. Training and Education
1. Ongoing Training:
- Regular Updates: Provide regular training and updates on chemical safety protocols to all laboratory personnel.
- Emergency Drills: Conduct periodic emergency drills to ensure readiness for chemical incidents.
2. Documentation:
- Record Keeping: Maintain records of chemical inventories, safety training, and incidents. Ensure that safety procedures are documented and accessible.
Conclusion
Chemical safety and handling protocols are crucial for maintaining a safe laboratory environment and protecting the health of individuals and the environment. By following proper procedures for PPE use, chemical storage, handling, and disposal, and ensuring ongoing training and education, you can minimize risks and prevent accidents. Adhering to these protocols not only ensures compliance with regulations but also fosters a culture of safety in the laboratory.