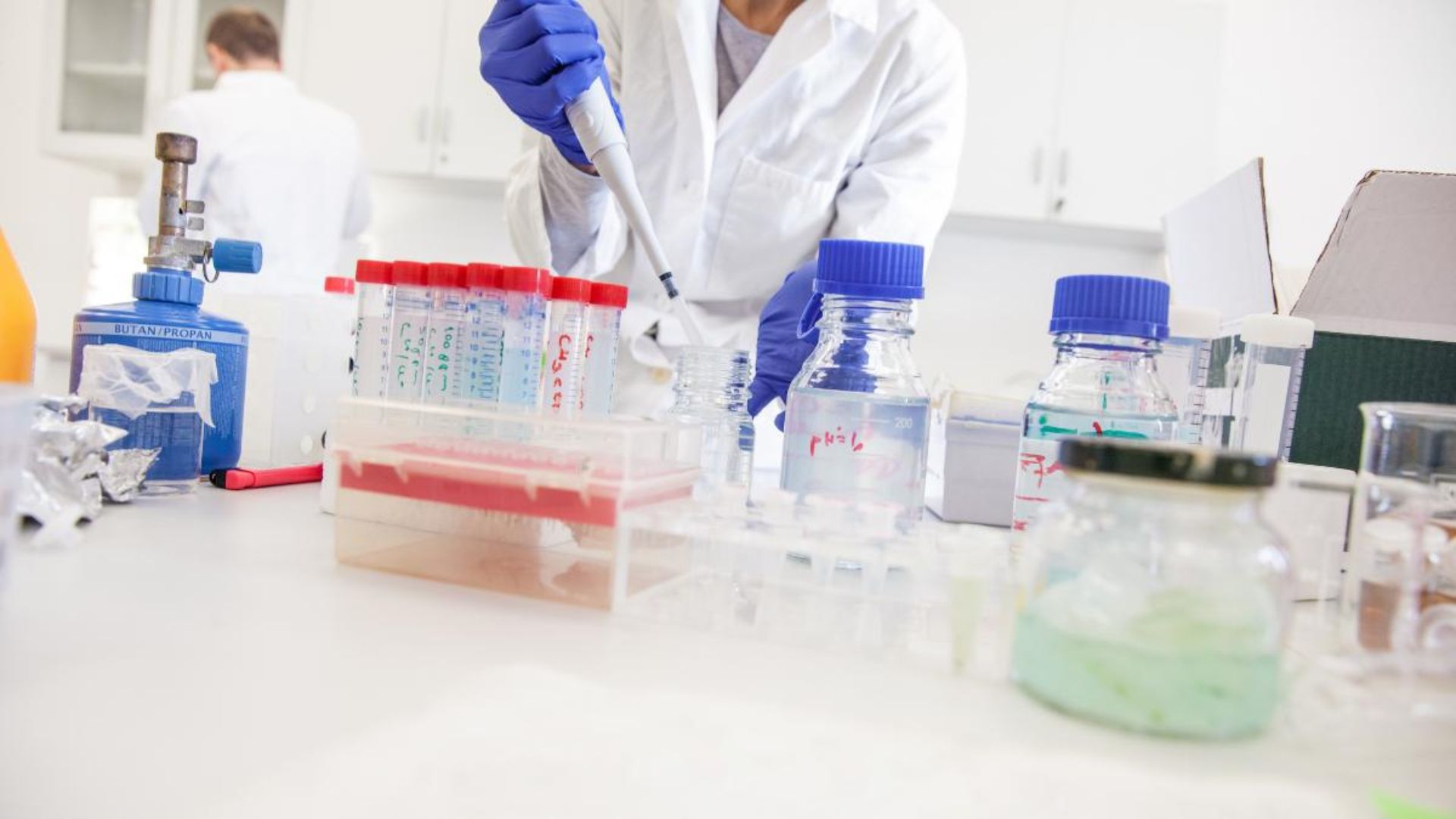
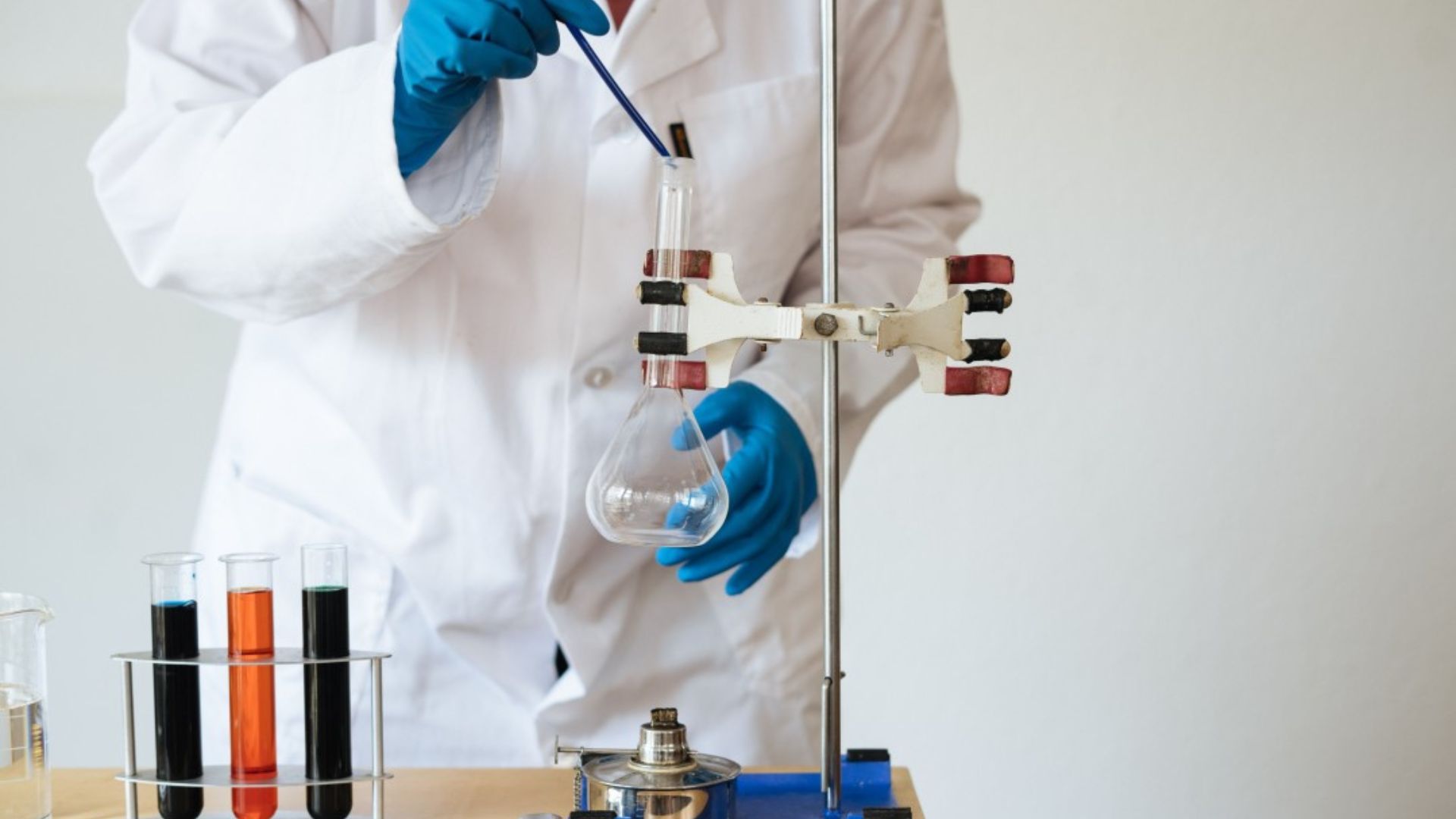
Chemical sample preparation is a crucial step in analytical chemistry. It ensures that samples are in the right condition for accurate testing and analysis. Here’s a detailed guide on the best methods for preparing chemical samples to achieve reliable results.
1. Understand the Sample Requirements
Before starting chemical sample preparation, it’s essential to understand the requirements of your analysis. Different methods are suited to various types of samples and analyses. Review the analytical method and its requirements to determine the appropriate preparation technique.
Chemical Sample Preparation
2. Sample Collection
Proper sample collection is the foundation of effective chemical sample preparation. Use clean, appropriate containers and avoid contamination. For liquid samples, use sterile syringes or pipettes. For solid samples, ensure that containers are dry and clean. Always label samples clearly with all relevant information.
3. Sample Homogenization
Homogenization ensures that the sample is uniform throughout, which is vital for accurate analysis. For liquids, shaking or stirring may suffice. For solids, grinding or milling can help achieve uniformity. Use clean equipment and avoid cross-contamination between different samples.
4. Sample Filtration
Filtration is necessary to remove particulates from liquid samples. This process can prevent clogging of analytical instruments and improve accuracy. Choose the appropriate filter type and pore size based on the sample’s characteristics. Regularly replace filters to maintain effectiveness.
5. Sample Dilution
Dilution is often necessary to bring the sample concentration within the instrument’s range. Prepare dilutions carefully, using accurate pipettes and volumetric flasks. Ensure that dilutions are mixed thoroughly and that the final volume is correct for accurate results.
6. Sample Extraction
Extraction is used to isolate specific compounds from a mixture. Techniques include liquid-liquid extraction, solid-phase extraction, and supercritical fluid extraction. Select the extraction method based on the nature of the sample and the compounds of interest.
7. Sample Derivatization
Derivatization can enhance the detection and analysis of compounds that are otherwise difficult to analyze. This involves chemically modifying the sample to improve its properties, such as volatility or detectability. Follow established protocols for the derivatization process to ensure consistency and accuracy.
8. Sample Preservation
To prevent degradation or alteration, preserve samples properly. Depending on the sample type, this might involve refrigeration, freezing, or the addition of preservatives. Always store samples in conditions that maintain their stability until analysis.
9. Sample Calibration
Calibration is crucial for ensuring accurate measurements. Prepare calibration standards that closely match the concentration and composition of the samples. Use these standards to calibrate your instruments, following the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal performance.
10. Sample Mixing
Thorough mixing of samples is necessary to ensure homogeneity. For liquids, use a vortex mixer or magnetic stirrer. For solids, consider using a mortar and pestle or an industrial mixer. Ensure that mixing is uniform and consistent for reliable results.
11. Sample Drying
For some analyses, drying the sample may be required. Use an oven, desiccator, or other drying equipment to remove moisture. Be mindful of temperature settings to avoid altering the sample’s chemical properties. Ensure that the sample is completely dry before proceeding.
12. Sample Acidification or Alkalinization
Adjusting the pH of a sample can be necessary to stabilize it or to facilitate certain reactions. Add acid or base as needed, and monitor the pH using a calibrated pH meter. This step is critical for samples where pH can affect the analysis.
13. Sample Homogeneity Testing
After preparation, test the sample to ensure it is homogeneous. This can involve sampling from different parts of the sample and analyzing them for consistency. Ensure that any variability is minimal to maintain the accuracy of your results.
14. Use of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Follow standard operating procedures for all sample preparation steps. SOPs ensure consistency and reliability in the preparation process. Regularly review and update SOPs to reflect best practices and any changes in procedures.
15. Documentation and Record Keeping
Document every step of the chemical sample preparation process. Record details such as sample collection methods, preparation techniques, and any issues encountered. Accurate documentation helps track the preparation process and ensures traceability for future reference.
Conclusion
Effective chemical sample preparation is vital for achieving reliable and accurate analytical results. By understanding sample requirements, using proper techniques, and following established protocols, you can ensure that your samples are well-prepared for analysis. Implementing these methods will help maintain the integrity of your results and contribute to successful outcomes in your research or testing.




