Chemical spills pose significant risks in industrial, laboratory, and even household settings. Quick, effective response is crucial to mitigate dangers to health, safety, and the environment. Understanding and implementing emergency procedures for chemical spills ensures preparedness and minimizes potential harm.

Emergency Procedures for Chemical Spills
Initial Assessment and Evacuation
When a chemical spill occurs, immediately assess the situation to determine the spill’s severity and potential hazards. Identify the chemical involved, the quantity spilled, and any immediate risks, such as fire, toxic vapors, or reactivity with other substances. If the spill poses an immediate danger to people in the vicinity, initiate an evacuation. Ensure that all personnel evacuate calmly and proceed to designated safe areas. Use alarms and emergency communication systems to alert others in the area.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for anyone involved in spill response. Depending on the chemical and the spill’s nature, appropriate PPE may include gloves, goggles, face shields, aprons, or full-body suits. Respirators or masks might be necessary for spills involving volatile or toxic substances. Ensure that PPE is readily available and that personnel are trained in its correct use and limitations.
Containing the Spill
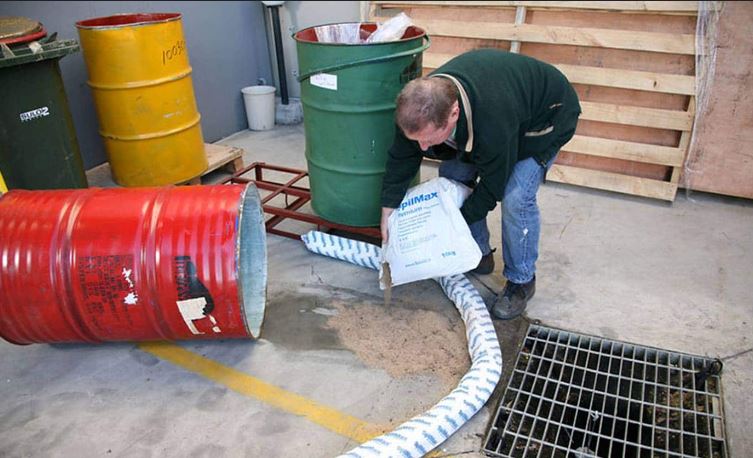
Containment is the next critical step to prevent the spill from spreading. Use absorbent materials, such as pads, socks, or booms, to encircle the spill and absorb the chemical. If the spill involves a liquid, create a barrier using dikes or absorbent materials to prevent it from reaching drains or spreading to other areas. For solid spills, carefully sweep up the material, minimizing dust generation. Proper containment limits environmental impact and reduces exposure risks.
Neutralizing and Cleaning Up
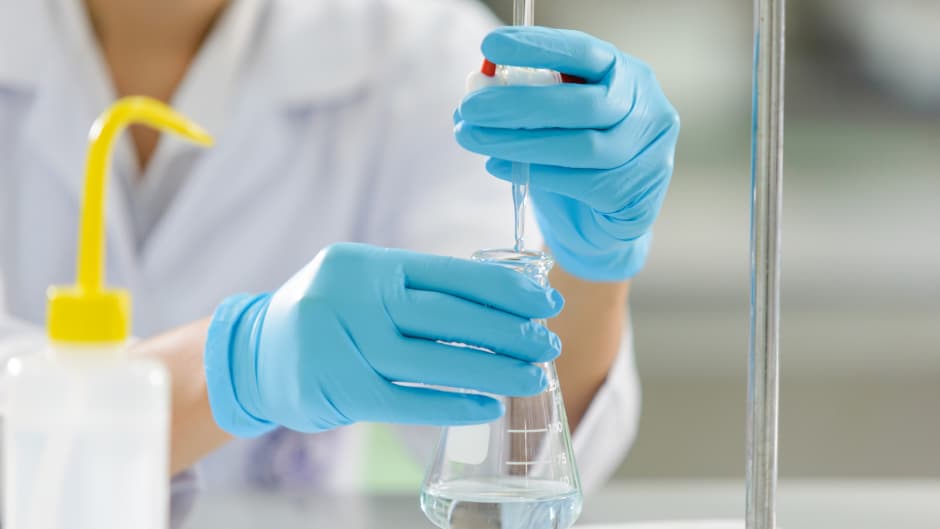
After containment, proceed with neutralization and cleanup. For acidic or basic spills, use neutralizing agents to render the chemical safe for handling. Follow specific procedures and guidelines for the neutralizing agents, as incorrect usage can cause dangerous reactions. Absorb and clean up the neutralized material using appropriate tools and containers. For hazardous or toxic chemicals, use specialized cleanup kits designed for the specific substance. Ensure that all waste materials are properly labeled and disposed of according to regulatory requirements.
Ventilation and Air Quality Control
Spills involving volatile or toxic chemicals may release harmful vapors or gases. Ensure proper ventilation to disperse these contaminants and maintain air quality. Use fans, exhaust systems, or open windows and doors to increase airflow and reduce vapor concentrations. In some cases, portable air scrubbers or filters may be necessary. Continuous monitoring of air quality ensures that it returns to safe levels before allowing personnel to re-enter the affected area.
Decontamination Procedures
Decontamination of personnel, equipment, and the affected area is essential to eliminate residual chemicals and prevent further exposure. Use appropriate decontamination solutions and procedures based on the chemical involved. Personnel involved in cleanup should undergo thorough decontamination before removing PPE. Clean and inspect all equipment used in the response to ensure no chemical residues remain. Proper decontamination protects health and prevents cross-contamination.
Documentation and Reporting
Thorough documentation and reporting of the spill and response actions are vital for regulatory compliance and future prevention efforts. Record details such as the chemical involved, the quantity spilled, the response actions taken, and the personnel involved. Include information on PPE used, containment and cleanup methods, and any injuries or exposures. Submit required reports to regulatory agencies and conduct a post-incident review to identify areas for improvement in spill response procedures.
Training and Preparedness
Regular training and drills ensure that personnel are prepared to respond effectively to chemical spills. Conduct training sessions covering spill response procedures, proper use of PPE, containment and cleanup techniques, and decontamination processes. Periodic drills simulate spill scenarios, allowing personnel to practice their response skills and identify any weaknesses in current procedures. Continuous training and preparedness build confidence and competence in handling chemical spill emergencies.
Conclusion
Effective emergency procedures for chemical spills are critical to ensuring safety and minimizing harm. By following a structured response plan that includes assessment, containment, neutralization, ventilation, decontamination, and proper documentation, organizations can manage spills efficiently and reduce associated risks. Regular training and preparedness further enhance the ability to respond to spills, promoting a safer environment for all.